How Air-Gap Backup and Tape-Based Technology Protect Against Cybercrime
Cybercrime is a prevalent topic in today’s news. It’s changing the way business is conducted to maintain data integrity and protection from theft. Data is the life blood of any organization; cybercriminals seek to exploit data from human as well as security vulnerabilities inherent to the software or hardware structures. Much of corporate data today needs to be protected via data compliancy regulations and standards.
One of the ways to provide this protection is by implementing an air-gap backup environment. An air-gap backup and recovery strategy is all about ensuring, at any point in time, that at least one copy of an organization’s data is disconnected, offline and unavailable for access. Thus, if the data has no connectivity with the internet or a LAN, it prevents the data from being attacked and this avoids corruption from hacking.
Today, many corporations and organizations employ a backup and recovery strategy known as 3-2-1. This has been around for a long time and is a very effective approach. When the methodology of air gap is added to this backup strategy, a copy of that data is not remotely accessible thus creating the concept of air gapping. As part of this solution, backup and recovery software is employed to back up multiple copies. The key is multiple copies, in some causes up to a ridiculous 500 copies, and immutability. With immutability, the data cannot be altered in any way. This strategy simply means having three copies of the data, two copies that are local but on different storage mediums (IE: DASD, VTS or magnetic tape) and one copy that is offsite and disconnected from the network and internet.
Magnetic Tape and Tape Technologies
As old school as magnetic tape might be, it’s really one of the preferred methods as far as one of the copies for the 3-2-1 strategy because it’s reliable. Studies have shown that magnetic tape can last for up to 30 years where hard drives on the average are roughly five years. Other reasons are scalability, cost effectiveness and longevity. Conversely, there are some drawbacks to magnetic tape as a backup medium (i.e. slower time to restore, high capex and it being an older technology). IBM is the leading tape storage vendor in the industry and has over 2x the market capture of any vendor. The air-gap backup topic has brought tape-based technology back into focus as a solid solution to protect against cybercrime. Tape is all about “offline” storage.
The air-gap solution is created when a tape cartridge is secured in offline storage as this is a medium that is not connected to the internet or network in any way. A hacker cannot corrupt or steal what they cannot access. Thanks to tape technologies, which have been around for a long time, the capabilities of software-defined storage give worldwide enterprises solid tools to define against cybercrime.
There has been a new directional focus, due to cybercrime, that’s purely driven by the ability to recover from logical data corruption. Especially with financial and healthcare institutions, there are government led requirements from industry regulators to ensure that protection is in place. Some of the industry regulators include:
- European Banking Authority
- U.S. National Association of Insurance Commissioners
- U.S. Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council
Logical data corruption is driven by many sources, but one top source has been internal bad actors that account for approximately 60% of the problem. Inadvertent user error and external cyberattacks round up the sources next. Additionally, there are many types of logical corruption that include things like malware, ransomware and payload launched viruses, selective manipulations, and internal actors intentional deletions. Copy solutions, being asynchronous or synchronous, aren’t aware of the content that’s being copied. Replication will happen even if the data has been corrupted since the copies look like perfectly fine I/O activity.
Explaining Air-Gap Backup
The overall objective of air-gap backup is to expand the scope of data protection to ensure that both cybersecurity and business continuity are protected. Air-gap backup should be a part of any high availability and disaster recovery solution. Ideally, air-gap backup provides immutability, isolation as well as granularity of the data protected. Multiple copies that are all recoverable should be spread across multiple volumes and if possible, on different storage systems. Recovery points should be designed to be made available on any set of the recovery volumes. This should not in any way affect production work. The data is secured to ensure it from deliberate or accidentally being compromised. Many entities actually wall off the disconnected copy via a locked room or cage to provide uncompromised access. Many of the actual DASD volumes have feature codes that provide a lock on the covers of the unit, again to prevent uncompromised access.
An air-gap backup solution should be an entire process geared toward handling several key items for the care of feeding of the system. It’s one thing to install software and hardware to support the process, but an actual process is the real need. Validation of the data enables early notification of a data corruption issue. Validation provides confirmation that the data is uncorrupted, or corrupted and further action is necessary. The corruption of data puts into action further steps to protect the corporation’s data.
Forensic analysis is performed to determine exactly what data is corrupted, when the corruption occurred and if it can be repaired with the backup copy. Surgical recovery is attempted once it’s verified that only certain areas of the data is in question. Finally, with a catastrophic recovery, it’s determined that the data corruption is extensive, and the entire environment will need to be restored. This is a situation where having that immutable air-gap backup copy will save the day!
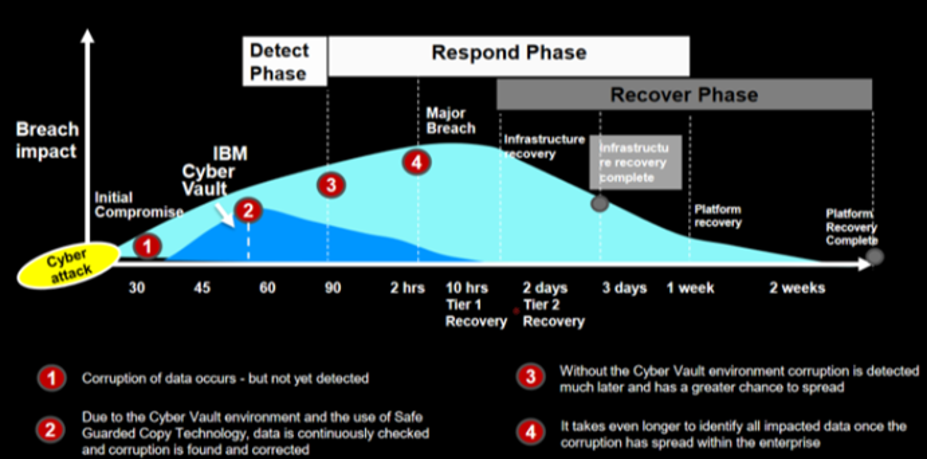
The IBM version of this solution is called IBM Z Cyber Vault (see Figure 1). The root construction is the DS8000 Safeguarded Copy feature built on logical copy protection (LCP) and an automated cyber vault.
IBM Z Cyber Vault:
- Exploits Safeguarded copy technology, DS8950F storage, z15 and GDPS services
- Regularly checks for data corruption
- Helps investigate the extent of the damage
- Assists with recovery
Protecting Data With Air-Gap Backup
In short, air-gap backup is not a new concept. With added corporate compliancy requirements, this methodology has been a go-to solution to provide unparallel protection against issues with data corruption. Data is the life blood of any organization and must be protected at any cost.
All information in this article is provided to you “as is” and represents the views of the authors. TechChannel cannot guarantee or imply absolute reliability, serviceability or function of the information herein.